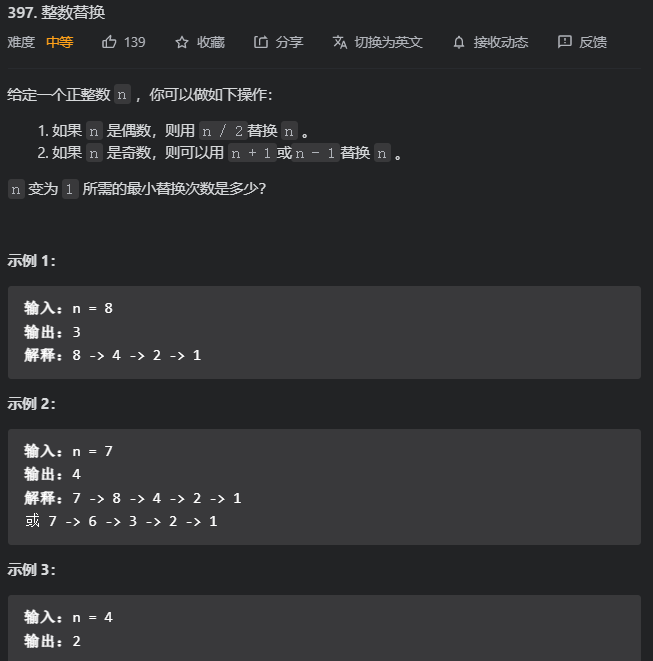
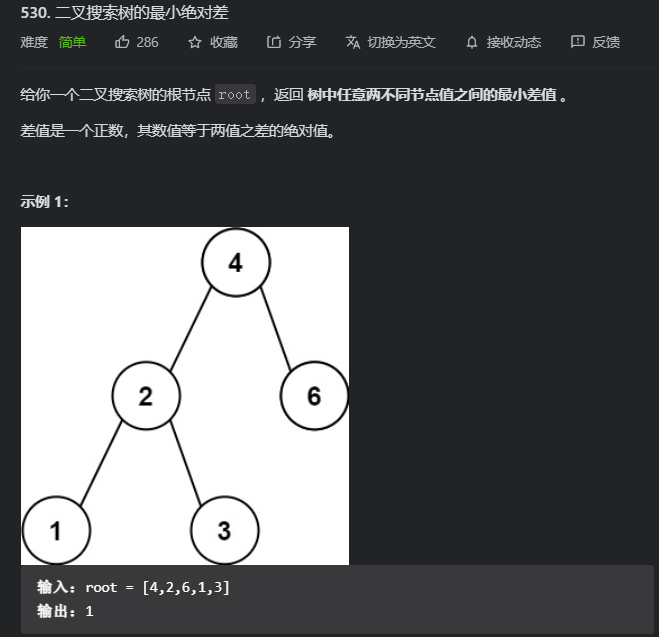
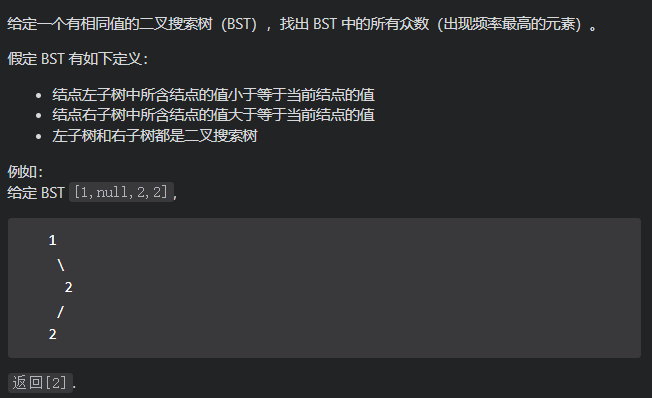
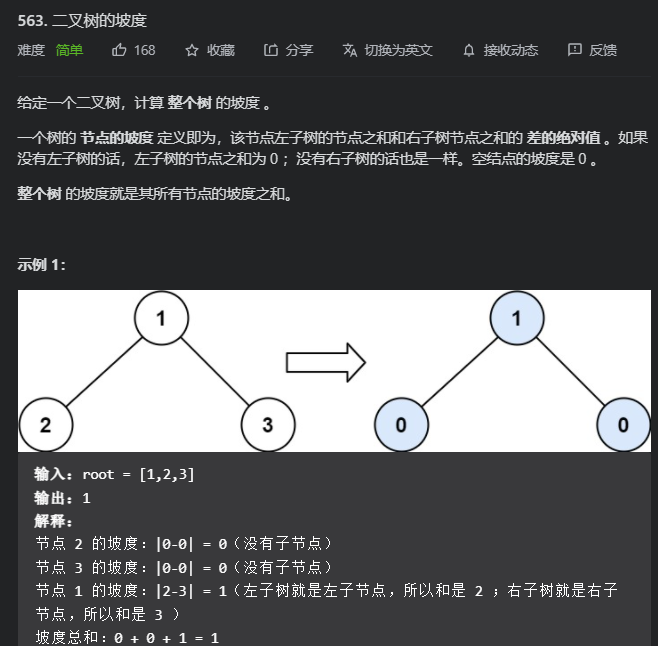
559. N 叉树的最大深度

今天的lc每日一题
题目很简单,但是我猛然间将现在的代码和以前的代码做了一个对比,有了新发现
下面是我今天的代码,我的代码思路是每递归深入一层,就更新一次深度(初始深度为1),最后的全局变量就是答案
1 | class Solution { |
这是我以前的代码,后序遍历,这就不是在求深度了,这是从底层往高层算,是在回溯,求的是高度,而二叉树的高度值与深度值大小相同,所以代码也就过了。
1 | class Solution { |
这再次印证了Carl的话,递归和回溯的区别,一个去一个回,是截然不同的