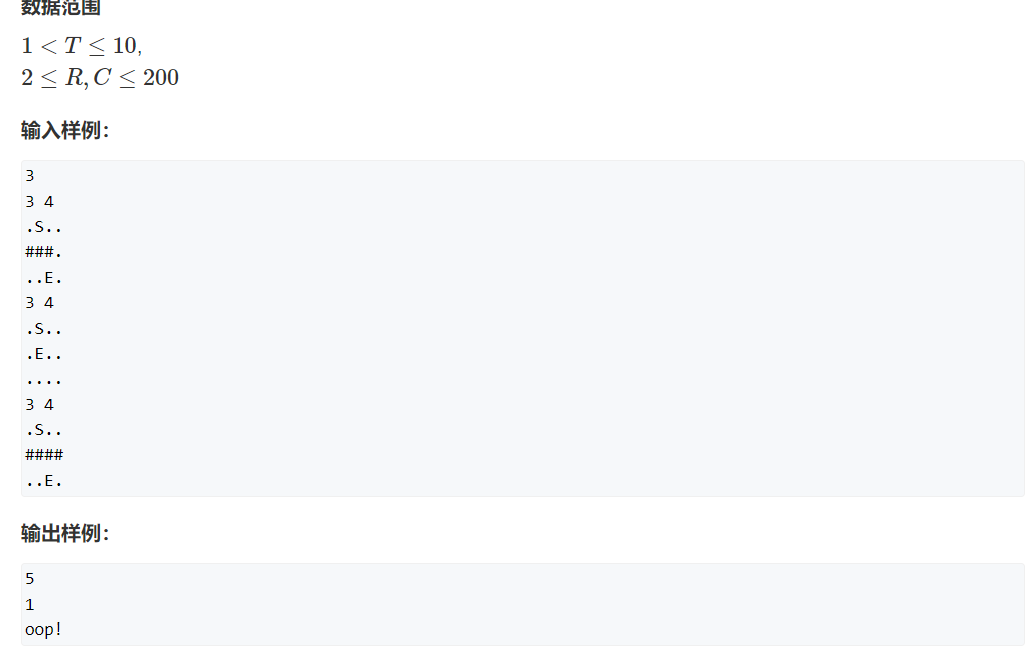
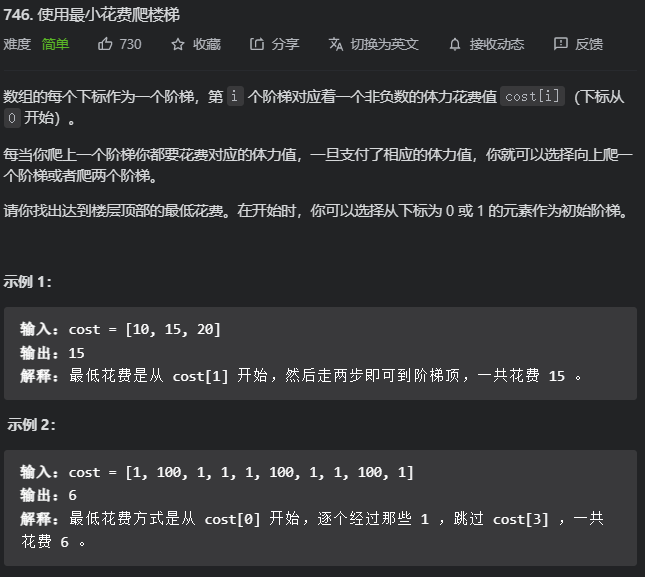
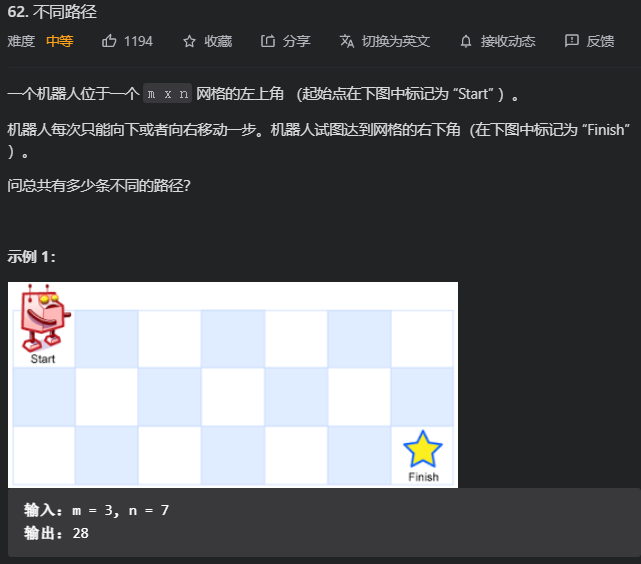
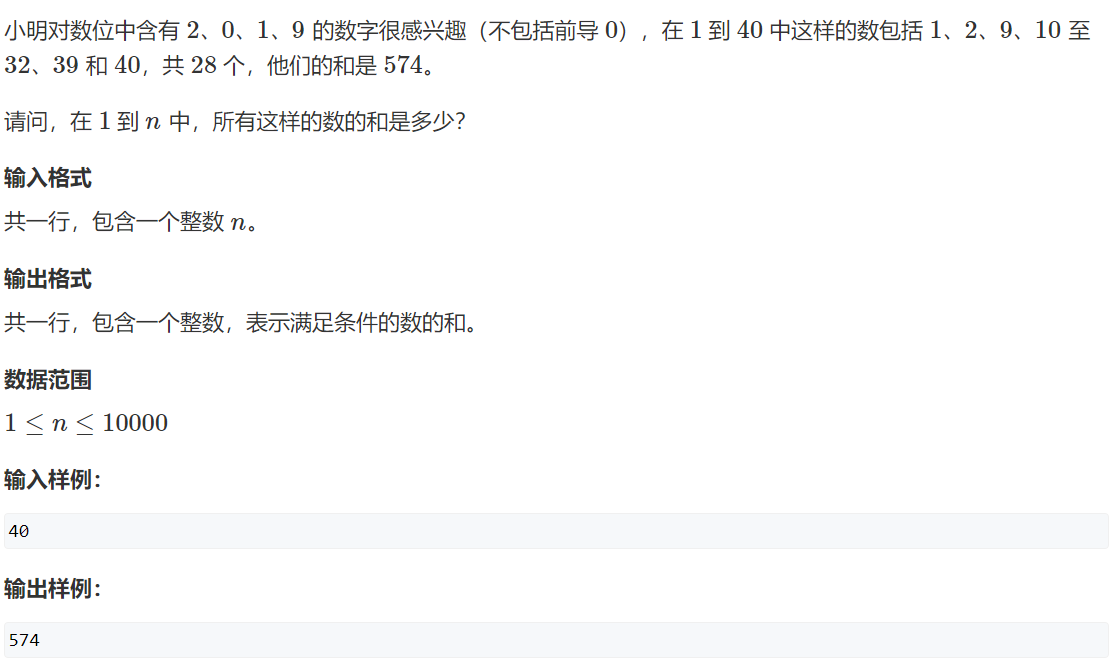
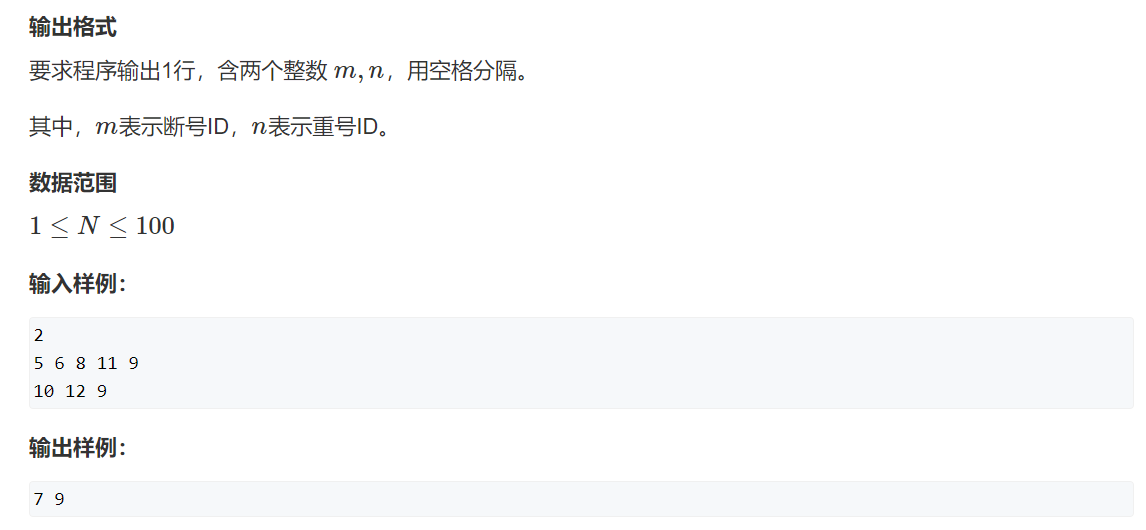
748. 最短补全词

简单签到题
1 | class Solution { |
js版本
1 | /** |
714. 买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费

为什么要minprice-fee 当我买完一次股票后, 如果它紧接着又上涨了, 那后面就不用出手续费了, 直到这个上涨区间断掉, 手续费只用扣掉一次, 这样就形成了局部最优解
1 | class Solution { |
Hydra blog

简单签到题
1 | class Solution { |
js版本
1 | /** |

为什么要minprice-fee 当我买完一次股票后, 如果它紧接着又上涨了, 那后面就不用出手续费了, 直到这个上涨区间断掉, 手续费只用扣掉一次, 这样就形成了局部最优解
1 | class Solution { |

思路是找到之前出现的最大下标和,如果当前下标与它相等,就存入答案数组中
1 | /** |
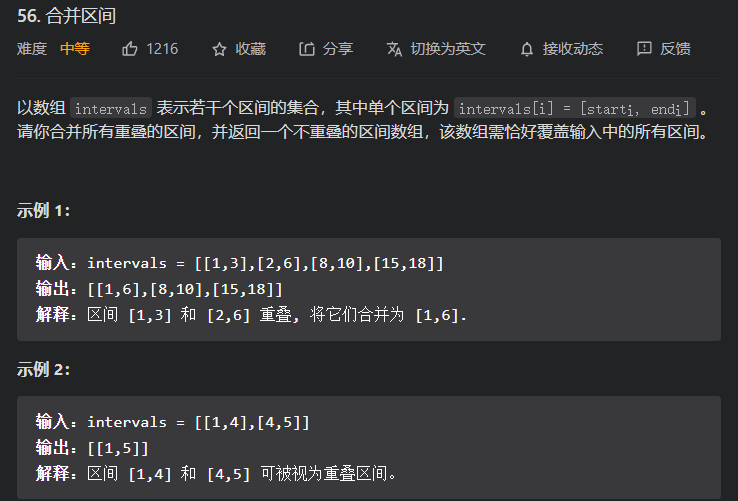
排序左区间, 然后比较右区间判断是否进行合并, 跟之前的弓箭射气球一题还是有区别的, 后面可以稍微总结一下
我不应该执着于用双指针解题, 研究了一下正确答案发现双指针不能确保第二个慢指针一直指向res的最后一个数组, j是随着i更新, 而不是res末尾
弓箭射气球题要求的是区间数量, 所以可以用右区间排序, 找右区间的交叉点贪心解决, 这题要合并区间就要左右端点同时考虑
1 | class Solution { |
附上js版本
1 | /** |
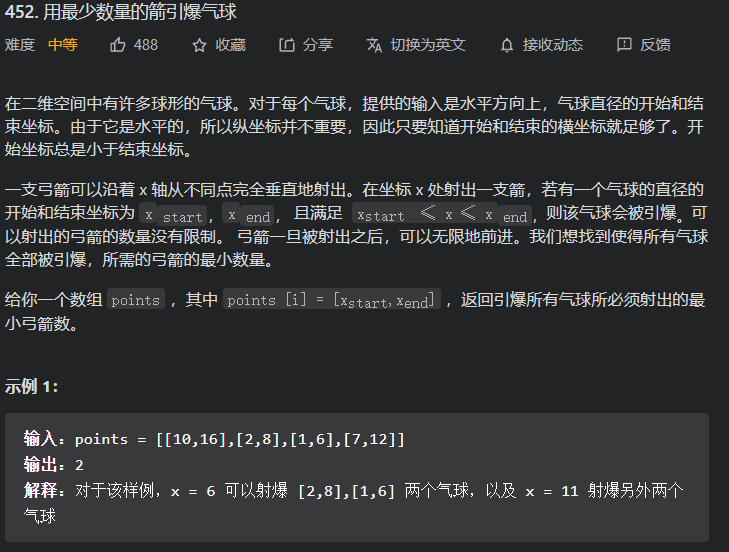
不断更新最大maxL, 每更新一次, 答案+1, 第一次更新是因为区间最少有一个, 再者这个循环比了n-1次, 最坏情况下我需要n支弓箭才行,所以+ 1
这题贪心在只要有两个以上的气球重叠, 就射爆它, 不用再考虑后面的情况
1 | /** |
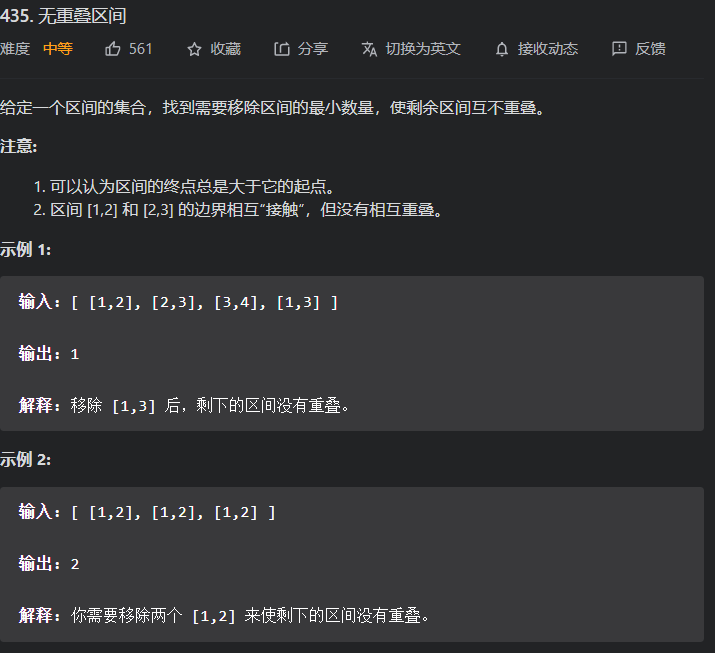
和上一题很相似,但是这题用了双指针
这题要考虑最后上一个区间对下一个的交叉情况, 并不断更新两个指针
1 | /** |

双指针+piar,技巧性题目
1 | #include<iostream> |

#define 命令是 C 语言中的一个宏定义命令 ,它用来将一个标识符定义为一个字符串
typedef 关键字来定义自己习惯的数据类型名称,来替代系统默认的基本类型名称、数组类型名称,后面有省略号
1 | #include<iostream> |

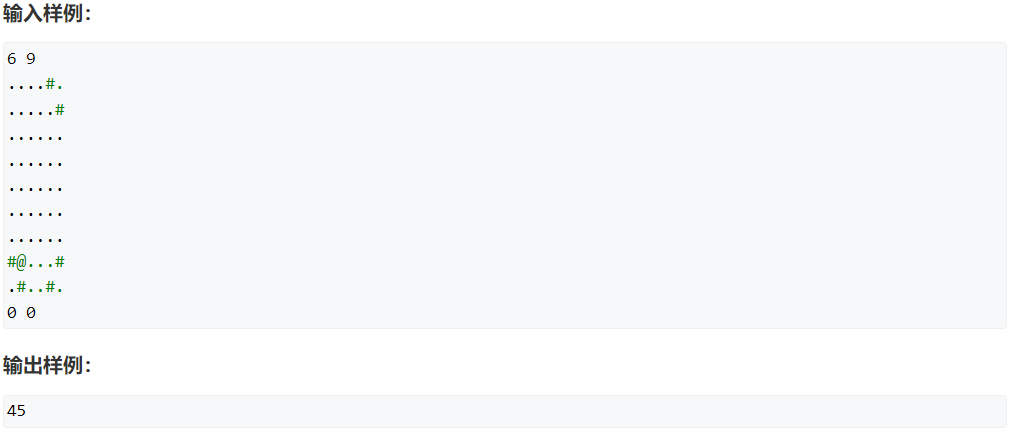
对于bfs搜索,要特别注意标记数组标记的位置,遵循开始点在哪赋值,后面就在哪赋值
比如这题。开始点在while循环之前就标记好了,然后再开始队列循环。同理,对于后面的点,也应该是先标记后从队列中取出来操作,所以就是在for循环中标记
1 | #include<iostream> |
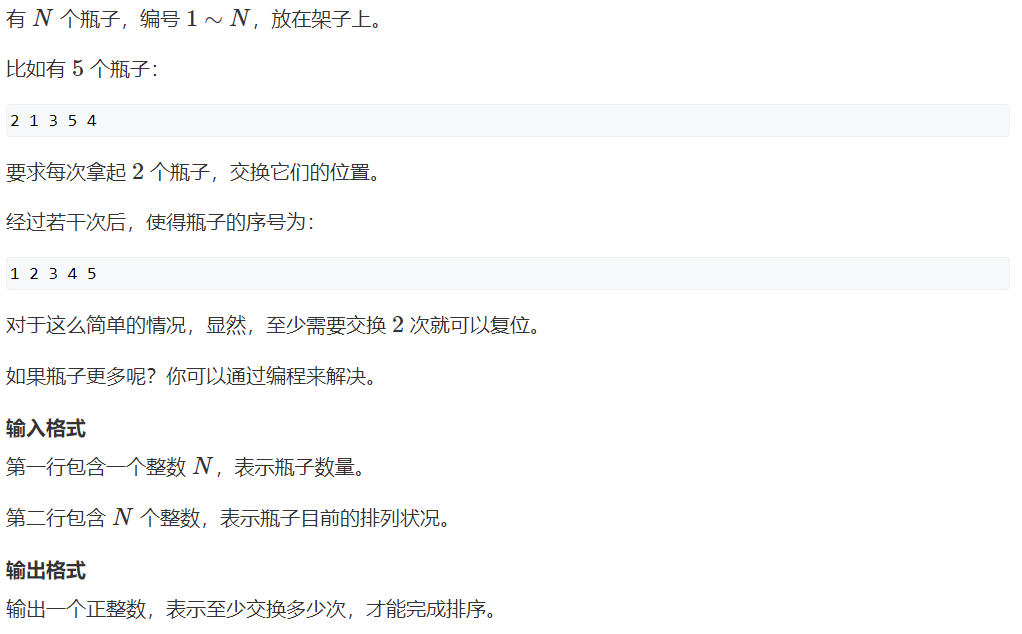
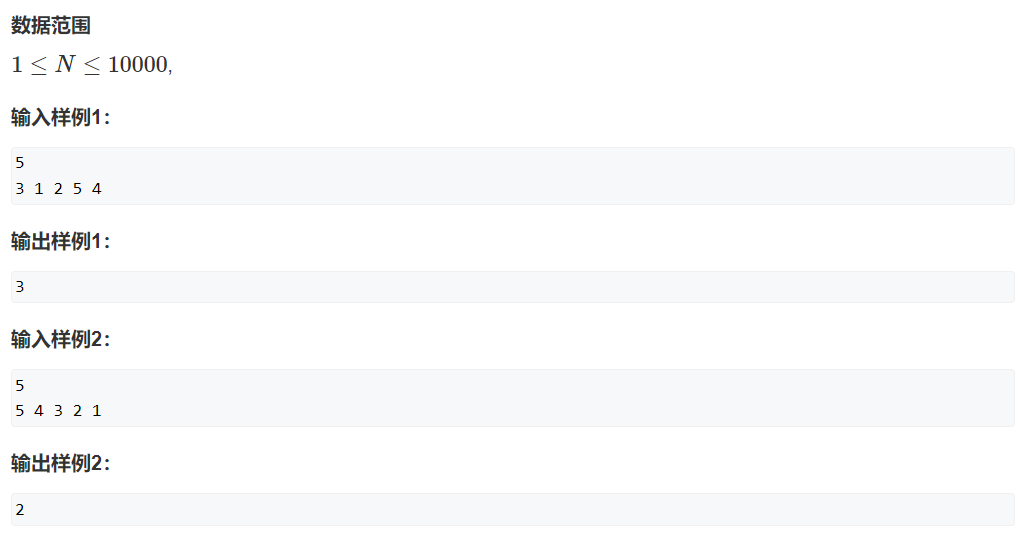
暴力法
1 | #include<iostream> |
这个题目很经典,建议深刻记忆
1 | #include<iostream> |

每日一题,贪心题
1 | var largestSumAfterKNegations = function(nums, k) { |
重刷leetcode的题,不定期更新(改用javascript刷题)
1 | /** |
写下面这题之前要搞清楚js中的二维数组如何定义
方法一:传统的定义方式
1 | //定义m行n列的数组,初始化为0 |
方法二:奇淫技巧
1 | //定义m行n列的数组,初始化为0 |
明天更
1.
推荐使用stringstream
1 | string result= ”10000”; |
如果你打算在多次转换中使用同一个stringstream对象,记住再每次转换前要使用clear()方法;
1 | #include <sstream> |
1 | 456 1 |
简单模拟, 今日打卡第一题
1 | #include<iostream> |

题目本身没有难度,就是考的输入
借这里强调一下scanf吧,scanf会留下回车,scanf的结束符在键盘上是【ctrl+z】,在文本中是EOF【END OF FILE】
1 | #include<iostream> |
yxc的代码用的sstream流,太神奇了
要强调几点
cin的结束符是回车,读取结束后回车仍然会保留在缓冲区中,会让下次的输入继续读取,如果还是cin,那就再留到下一次,空格是不会处理的,scanf同理
getline则是先读取一行,如果碰到回车就会结束,但不会进入缓冲区。所以就可以用getline单独处理cin留下的空格
1 | cin >> x; //用x保存输入内容,并留下回车 |
stringstream用于分割被空格,制表符号分割的字符串
1 | #include<iostream> |
1 | i |
1 | #include <cstring> |


模拟题,虽然简单,但是题目看了半天,宛如智障
1 | #include<iostream> |

首先找规律,然后进行模拟
1 | class Solution { |
关于二分法,一般是确定想找的条件,然后再举出它的相反的条件(比如求大于等于target的第一个数,就举出小于target的式子,然后破坏它)
看下面一段代码
1 | while(l < r){ //l是区间的左端点, r是右端点, 都是能取得到的左闭右闭区间【l,r】 |
菜到令人发指的地步, 写了半天二分,结果发现原来是二分思路的问题,不是我的问题,lower_bound函数在失败时会返回last,而我手写的二分没有这个功能,误入歧途了
1 | #include<iostream> |
经过这么一遭,算是加深二分的印象了,想要求什么就直接二分什么,不要曲线救国

简单dp题,有一点细节要注意
1 | #include<iostream> |
1 | #include<iostream> |
1 | #include<iostream> |
一段时间不写动态规划, 跟个傻子一样
1 | #include<iostream> |
所有的实例中的所有 jQuery 函数位于一个 document ready 函数中:
1 | $(document).ready(function(){ |
简洁写法(与以上写法效果相同):
1 | $(function(){ |
JavaScript 入口函数:
1 | window.onload = function () { |
jQuery 入口函数与 JavaScript 入口函数的区别:
jQuery 选择器允许您对 HTML 元素组或单个元素进行操作。
jQuery 选择器基于元素的 id、类、类型、属性、属性值等”查找”(或选择)HTML 元素。 它基于已经存在的 CSS 选择器,除此之外,它还有一些自定义的选择器。
jQuery 中所有选择器都以美元符号开头:$()。
jQuery 元素选择器基于元素名选取元素。
在页面中选取所有
元素:
1 | $("p") |